The urinary system, also known as the renal system, plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis by regulating fluid balance, electrolytes, and the removal of waste products. It comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Like any other system in the body, the urinary system is susceptible to a variety of diseases and disorders. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of urinary system diseases is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. This blog delves into the common signs and symptoms associated with urinary system diseases, helping you understand and identify potential issues early.
Overview of the Urinary System
Before discussing the diseases, let’s briefly review the components of the urinary system and their functions:
- Kidneys: These bean-shaped organs filter blood to remove waste products and excess substances, forming urine.
- Ureters: Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: A muscular sac that stores urine until it is excreted.
- Urethra: The tube through which urine exits the body.
Common Urinary System Diseases
Several conditions can affect the urinary system. Some of the most common include:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections that can affect any part of the urinary system, but most commonly the bladder and urethra.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): A long-term condition where the kidneys do not work as well as they should.
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): A sudden episode of kidney failure or damage.
- Interstitial Cystitis: A chronic condition causing bladder pressure, bladder pain, and sometimes pelvic pain.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate gland in men, which can affect urination.
Recognizing the Symptoms
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are among the most common urinary system diseases. They occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing infection. Symptoms can vary depending on the site of infection:
- Bladder (Cystitis):
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain or burning sensation during urination (dysuria)
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Lower abdominal pain
- Urethra (Urethritis):
- Burning sensation during urination
- Discharge from the urethra
- Itching or irritation at the urethral opening
2. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can cause severe pain and discomfort. They form when there is a decrease in urine volume or an excess of stone-forming substances in the urine. Common symptoms include:
- Intense pain in the back or side, usually on one side
- Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin
- Painful urination
- Pink, red, or brown urine (hematuria)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urination or a persistent need to urinate
- Fever and chills (if an infection is present)
3. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
CKD is a progressive condition that can lead to kidney failure if not managed properly. Early stages often have no symptoms, but as the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet (edema)
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent itching
- Changes in urination (frequency and quantity)
- Muscle cramps and twitching
- Chest pain, if fluid builds up around the heart
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
4. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
AKI is a sudden loss of kidney function, often reversible if treated promptly. Symptoms of AKI can include:
- Decreased urine output
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and around the eyes
- Fatigue and confusion
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain or pressure
- Seizures or coma in severe cases
5. Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
IC, also known as painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic condition characterized by bladder pain and frequent, urgent urination. Symptoms include:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- A persistent urge to urinate, often in small amounts
- Pain or discomfort during intercourse
- Pain that worsens with a full bladder or during menstruation
- Relief after urinating, but the need to urinate returns quickly
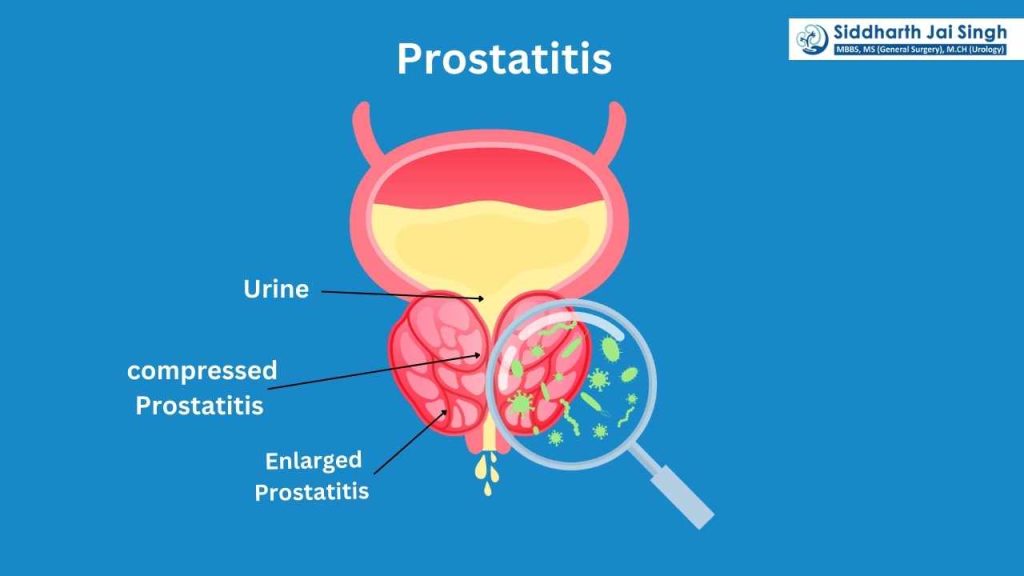
6. Prostatitis
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland and can be acute or chronic. Symptoms vary based on the type:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis:
- Severe pelvic or lower back pain
- Fever and chills
- Painful urination
- Difficulty urinating or urinary retention
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis:
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Painful ejaculation
- Persistent UTI symptoms
- Frequent urination
- Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome:
- Chronic pain in the pelvic area
- Painful urination and ejaculation
- Urinary frequency and urgency
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing the symptoms of urinary system diseases is the first step towards seeking appropriate medical care. You should see a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent or severe pain in the abdomen, back, or sides
- Blood in the urine
- Painful or difficult urination
- Frequent urination, especially if accompanied by pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Unexplained fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or around the eyes
- High fever with urinary symptoms
How Doctors Figure It Out
If you go to the best urinary problem doctor in Siliguri, they’ll likely run some tests. They might ask for:
- Urine Tests: Checks if there’s anything weird like bacteria or blood in your pee.
- Ultrasound: They might use this to take a quick peek at your kidneys or bladder.
- CT Scans: This one gives a more detailed look inside to find out what’s causing the problem.
- Cystoscopy: Sometimes they’ll use a tiny camera to look directly into your bladder.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing urinary system diseases effectively. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Urinalysis: To check for signs of infection, blood, or other abnormalities.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to visualize the urinary tract.
- Blood tests: To assess kidney function and detect underlying conditions.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra.
Treatment options vary depending on the specific disease and its severity. They may include:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like UTIs and bacterial prostatitis.
- Pain relief: Medications to manage pain associated with conditions like kidney stones and IC.
- Surgery: To remove kidney stones, repair structural abnormalities, or address severe cases of prostate enlargement.
- Lifestyle changes: Diet modifications, increased fluid intake, and other lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and prevent recurrence.
- Dialysis: For advanced CKD or AKI when kidney function is significantly impaired.
- Medication: To manage underlying conditions like high blood pressure or to slow the progression of diseases like CKD.
Preventive Measures
Preventing urinary system diseases involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and being vigilant about urinary health. Some preventive measures include:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water to flush out toxins and prevent stone formation.
- Hygiene: Practicing good personal hygiene to reduce the risk of infections.
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting salt, caffeine, and alcohol intake.
- Regular check-ups: Monitoring kidney function and overall urinary health, especially if you have risk factors like diabetes or hypertension.
- Avoiding irritants: Reducing the intake of bladder irritants such as spicy foods, carbonated beverages, and artificial sweeteners.
- Managing chronic conditions: Effectively controlling conditions like diabetes and hypertension to prevent kidney damage.
Conclusion
Understanding the common signs and symptoms of urinary system diseases is essential for early detection and treatment. By being aware of these symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention, individuals can manage their conditions more effectively and prevent serious complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and monitoring urinary health are key steps in preventing urinary system diseases. If you experience any concerning symptoms, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. Your urinary health is vital to your overall well-being, and proactive care can make a significant difference.

